Solutions

With the aim to conduct value-creating asset management, the foundation is acting as a long-term investor with concentration in large ownership stakes in a limited number of portfolio companies with good value potential realized through active ownership.
Active ownership is exercised mainly through board representation and continuous evaluation of the companies and their boards.
We believe it is in the best interests of the companies in which we invest to adopt best practice in corporate governance where each company can be managed for the long-term interests of its shareholders.
We seek to be good, long-term stewards of the investments which we manage.
Our major responsibility in this regard is to ensure that company boards are functioning well in their role as a fundamental expression of our stewardship responsibilities.
Our core stewardship principles:
Responsible Care
Attitude to act in the interest of all stakeholders
Harmony of Interests
A willingness to put the interests of others ahead of their own
Good Judgment
The best use of opportunities for the present and commitment to safeguard the future
Fairness
Ensuring that revenues are distributed in a way that corresponds to sustainable future
Mutual Confidence
All stakeholders should behave in such a way as to not undermine the stewardship process
Employee co-ownership is the model in which the share capital of a business is partly owned by its workforce either through:
- direct (individual) share ownership
- shares held in foundation on behalf of and for the benefit of employees
The popularity of employee co-ownership is based on the growing evidence of its benefits and are characterised by their higher productivity,
greater levels of innovation essential impact on organizational performance and individual wellbeing.
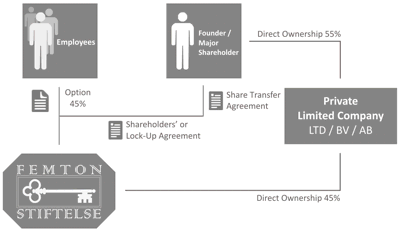
for Founder or Major Shareholder
- Greater entrepreneurship, innovation, talent attraction and retention
- Employee co-ownership is a way to preserve the integrity and continuity of the business
- Employee buy-out is one of the main business succession options for company owner
- Employee buy-outs tend to have a better record of sustainability
- A durable solution in case of handing over the family business to the next generation,
acknowledging the contribution of employees
for Employees
- Ownership with people who know the business and helped to build it up
- Owning company makes employee less likely to quit, more committed to work, more motivated and involved
- Higher levels of job satisfaction, feel a greater sense of achievement and increased wealth
- Improved job security
- Employee co-owned business tend to be better place to work
Employee co-ownership is an incredibly effective ownership model that works around the world, across a whole range of sectors and at any stage in the life of a business from start up to mature businesses seeking a viable succession route.
Employee co-ownership can be implemented easily and can be readily tailored to the circumstances of an individual organisation.
EMPLOYEE CO-OWNERSHIP: Concept, Design, Governance
A Board of Directors - a group of individuals that are elected as representatives of the stockholders - is a legal requirement almost for every company. For the privately owned company, the Board usually consists of the shareholders and/or a few family members and trusted persons.
As a business grows, the need for information and knowledge sharing, planning and delegation increases. A properly constituted Board is one body the shareholder can turn to for advice and assistance. A Board can offer the shareholder a much needed source of guidance in developing a long-term strategy.
In general, the Board makes decisions on shareholders' behalf, determines the strategic orientations of the company's activities and ensures their implementation. The issues that also fall under Board's control include the hiring and firing of executives, dividend policies, options policies, and executive compensation.
Certain responsibilities are delegated to Board Committees, which assist the Board in carrying out its functions and ensure that there is independent oversight of management and control. Usually, a Board may or should have at least three committees: nomination, audit and remuneration.The Board may appoint further committees if necessary.
We help shareholders in corporate governance by define Board constitution and setup decision-making process.
Improve the Board's overall effectiveness and efficiency by:
- Setup/review Board structure, clarify roles and responsibilities
- Develop governance policies
- Design Board processes in recruitment, evaluation and succession planning
- Develop annual work plans for the Board and its committees
The ROLE of the BOARD: Strategy and Effectiveness